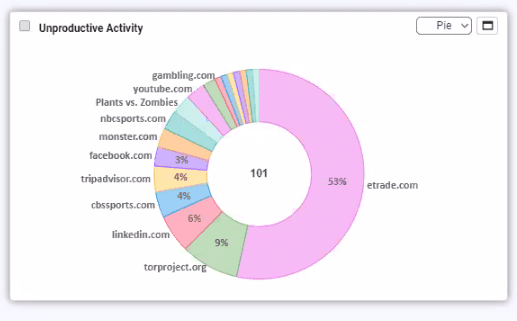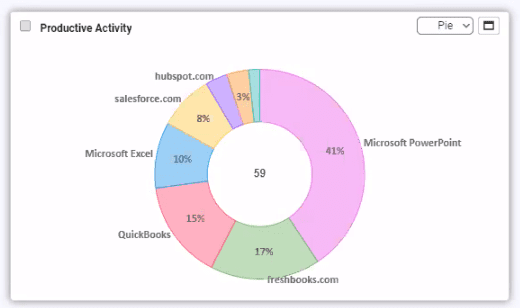
According to the ISO/IEC 27001 standard, Cybersecurity Governance is the system by which “an organization specifies the accountability framework and provides oversight to ensure that risks are adequately mitigated.” On the other hand, Cybersecurity Management is the process used to ensure that the right controls are implemented.
In general, Cybersecurity Governance implies going through several steps:
#1: A Well-devised Cybersecurity Strategy
Good cybersecurity governance can’t happen without a clearly defined risk management strategy with well-set goals and policies. Before implementing an effective strategy, the organization must understand the cybersecurity risks most likely to affect business operations and why.
Once you complete this step, identify the main needs and objectives to include in the strategy. This leads to correctly identifying the resources needed and the key performance indicators.
#2: Creating Standardized Processes
It is crucial for organizations to establish repeatable (or standardized) processes in order to be consistent about implementing the cybersecurity strategy. For instance, if you use cloud services to store important data, it is important to create backups, keep the system up to date, and stay informed on possible threats.
By keeping consistent watch over the health of your systems, you make sure there is no room for security breaches and shortfalls. Define these processes clearly to avoid any confusion or missed steps.
#3: Enforcement & Accountability
Who will take care of backups and who will constantly check if the systems are up to date?
What are the steps every employee must go through before logging in to the company network from a remote location?
Cybersecurity governance is about delegating responsibility for various tasks. It’s also about educating employees, managers, and higher-ups about their own responsibility and keeping them accountable if something does happen.
A great example of cybersecurity governance comes from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Risk Management Framework (RMF). They use a tiered approach that promotes integrating and adapting various cybersecurity methods as a system grows and develops. Constantly monitor the system and involve all decision-making levels in the process.
#4: Involving Leadership
The only way to implement a successful enterprise-wide cybersecurity strategy is with the support and leadership of the top decision-makers. They must ensure all processes are respected, followed properly, and held accountable.
In addition, they are also the ones that must ensure access to resources and information for all the people involved in the cybersecurity process.
Organizations that understand cybersecurity is a process that requires strategy and consistency, can lower their risk exposure and keep any damage at a minimum.
If your organization is struggling with implementing proper Cybersecurity management and governance, our specialists have the necessary knowledge and experience to provide you with guidance and resources. We can perform an analysis of your business risk and run vulnerability assessments to create a roadmap that can serve as the foundation of your cybersecurity strategy. If you require outside help in implementing a mature Cybersecurity program, we have the people, tools, and processes to supplement your program as well.
If you have questions about cybersecurity governance, don’t hesitate to reach out to our specialists.